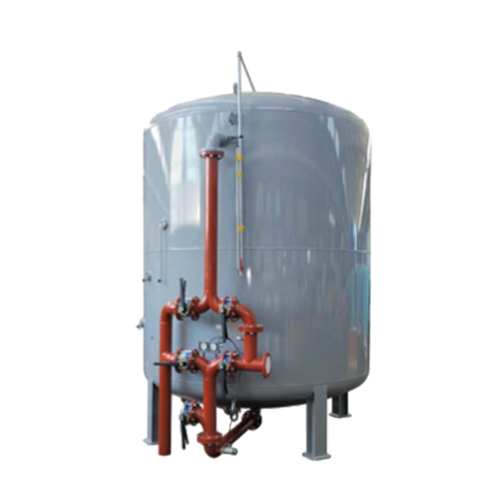
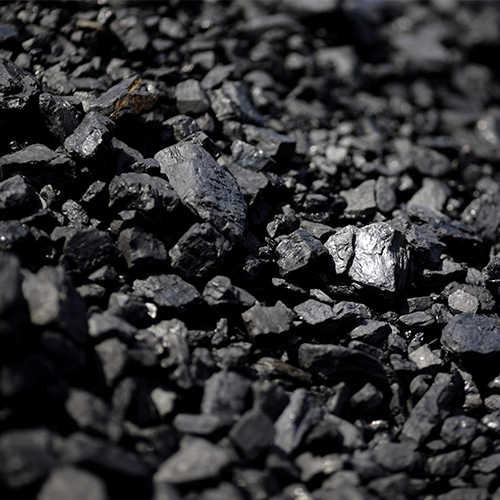
A familiar adsorption technology that is frequently applied for the removal of dissolved substances from water is activated carbon filtration.
The technology is exceptionally well-suited for the removal of colour, odour and flavour substances and for the removal of organic substances, pesticides and medicinal waste.
It is further applied for the catalytic conversion of oxidative substances such as chlorine, as well as in combination with advanced oxidation processes. Finally, activated carbon filtration can be utilized as a biological purification step.
Activated carbon filtration is often applied in the production of drinking and process water, and for the sanitation and purification of polluted groundwater.
The technology is characterized by the following advantages:

Operation activated carbon filtration
For active carbon filtration, the filter bed consists of grain-shaped activated carbon particles (GAC = Granular Activated Carbon). The activated carbon particles have a porous microstructure with a very large internal surface. The structure is ideal for removal of dissolved substances from the water on the basis of adsorption. With the adsorption process, attachment of substances to the (internal) surface of the grains occurs.
The degree of removal depends, among other things, on the molecule size, the molecule mass, the polarity and the concentration of the particles to be removed that is present, as well as the temperature and the contact time used.
Despite the fact that the primary operation of activated carbon filtration is focused on the removal of dissolved substances from the water, suspended particles can also be removed from the water by mechanical filtration. This can, however, cause fouling of the activated carbon grains with suspended particles that are too large, so that the absorption is hindered.
Activated carbon has a strong catalytic effect on the conversion of oxidizing substances such as free chlorine and peroxide. This means that vulnerable equipment, such as reverse osmosis (RO) installations, must be protected from these substances. The activated carbon filter will be placed before the RO installation in the process.
For application as a biologically activated filter, a biological break-down process of nutrients takes place. This means that the filtered water is more biologically stable. The porosity of the activated carbon is used here as a carrier for biomass.
The operation of the activated carbon filter can be compared with the operation of a discontinuous sand filter. Flow through the filter bed takes place from top to bottom. For a rinse, the flow is reversed, upwards, through the filter with water, whereby accumulated suspended particles are removed, and the bed itself will be ‘classified’, meaning that worn out activated carbon particles will also be rinsed away.
For biological activated carbon filtration, the back rinsing has to be done in a very controlled way in order not to completely rinse away the accumulated biomass.
With the back rinsing, the adsorbed substances are not removed. Over time, the activated carbon therefore becomes saturated with the adsorbed substances. There are then two options: replacement of the carbon bed, or – for large filters – regeneration and supplementation of the carbon bed. Regeneration will be done by the supplier of the activated carbon. It is a thermal process whereby the carbon particles will be ‘washed’ with hot air or steam at a temperature of about 800C.
Experience RWB
RWB has a great deal of practical experience with activated carbon filtration. The technology has been successfully applied and integrated in different drinking water and process water projects.
With our standardized line for activated carbon filtration, RWB can offer you an immediate solution for production of safe water.
RWB combines activated carbon filtration with ceramic membrane filtration. In this process, a layer of powder-form activated charcoal (PAC – Powdered Active Carbon) is applied to the ceramic membrane. The hybrid process combines the advantages of activated carbon and ceramic membrane filtration. An attractive application of this hybrid process is the removal of medicinal residues and pesticides from secondary effluent. The clean water from this purification step can be safely reused.
Realized projects
More information about activated carbon filtration?
Feel free to contact us via the number below or use the contact form.